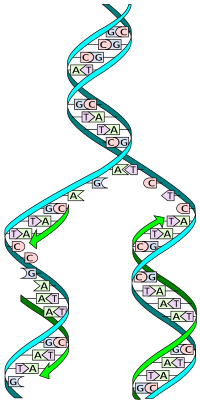
 DNA replication: The double helix is 'unzipped' and unwound, then each separated strand (turquoise) acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand (green). Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices.
DNA replication: The double helix is 'unzipped' and unwound, then each separated strand (turquoise) acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand (green). Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices.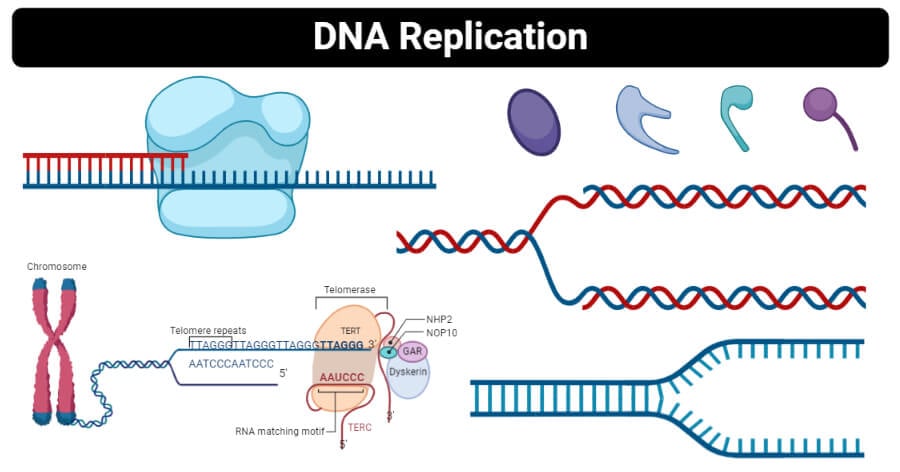 Summary: DNA replication takes place in three major steps. Assembly of the newly formed DNA segments. During the separation of DNA, the two strands uncoil at a specific site known as the origin. With the involvement of several enzymes and proteins, they prepare (prime) the strands for duplication.
Summary: DNA replication takes place in three major steps. Assembly of the newly formed DNA segments. During the separation of DNA, the two strands uncoil at a specific site known as the origin. With the involvement of several enzymes and proteins, they prepare (prime) the strands for duplication.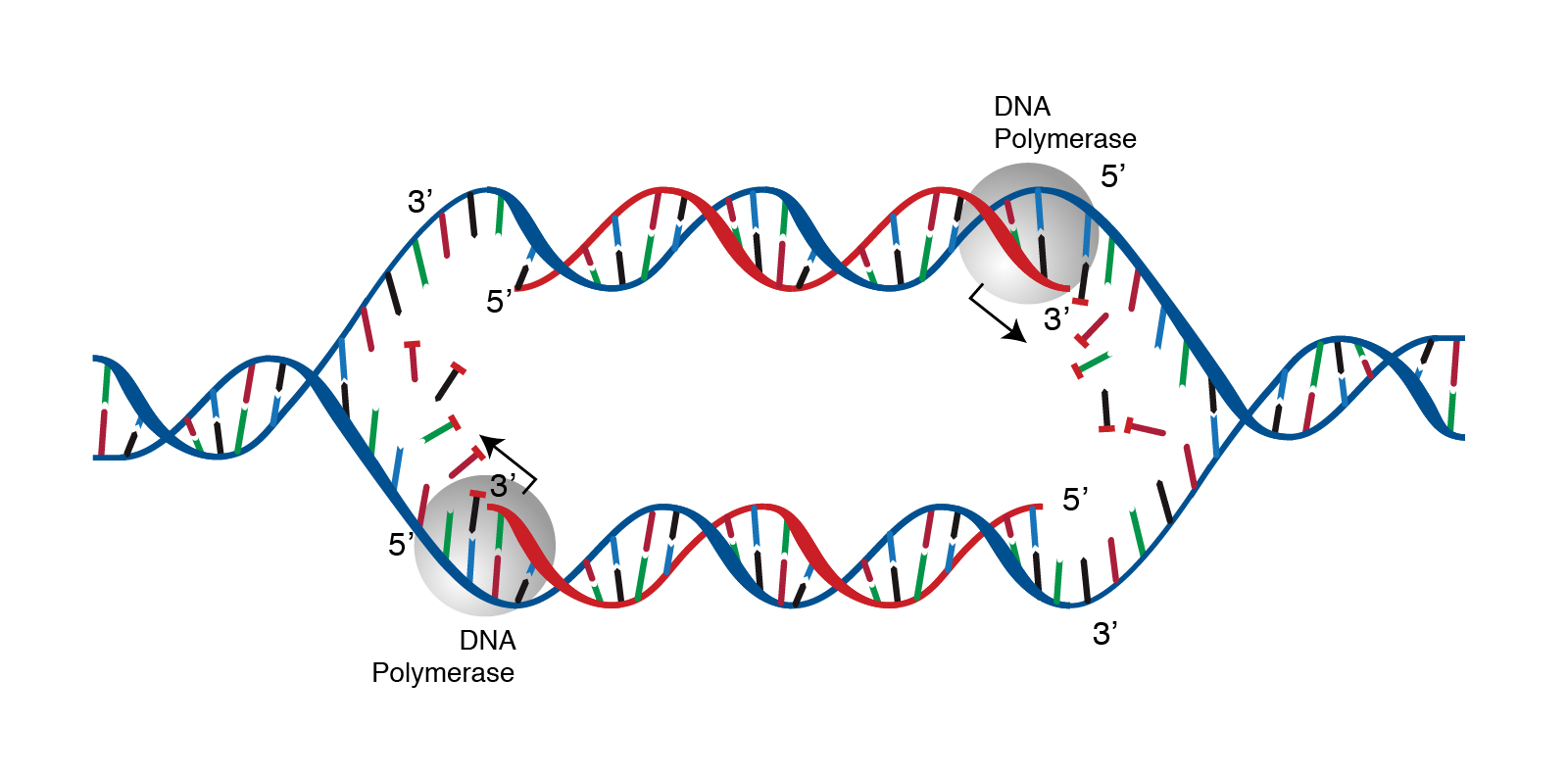 DNA replication is the process by which the genome’s DNA is copied in cells. Before a cell divides, it must first copy (or replicate) its entire genome so that each resulting daughter cell ends up with its own complete genome.
DNA replication is the process by which the genome’s DNA is copied in cells. Before a cell divides, it must first copy (or replicate) its entire genome so that each resulting daughter cell ends up with its own complete genome./DNA_replication_elongation2-e38fc92e8ad74586bfe0443d7490d3ce.jpg) DNA replication is the process in which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It is vital for cell growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms as it helps with the transmission of genetic information.
DNA replication is the process in which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It is vital for cell growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms as it helps with the transmission of genetic information. In this article, we shall discuss the structure of DNA, the steps involved in DNA replication (initiation, elongation and termination) and the clinical consequences that can occur when this process goes wrong.
In this article, we shall discuss the structure of DNA, the steps involved in DNA replication (initiation, elongation and termination) and the clinical consequences that can occur when this process goes wrong.